One of the ways to access data in the operator services is by REST API. To protect the endpoints, an authentication and authorization system is implemented by adding a layer of auth middleware. JWT (Json Web Tokens) is mainly used for the authentication system and privilege codes are used to validate the authorization for endpoint access.
User Service is a service that handles user management and also as the authorization server for all services. As an authorization server, this service handles all requests from other services that requires authorization. a gRPC method ValidateAccess handles endpoint access authorization. The method requests for token, privilege code, and IP address for different layers of authentication:
message ValidateAccessRequest {
string token = 1;
string privilege_code = 2;
string ip_address = 3;
}
message ValidateAccessResponse {
bool isAllowed = 1;
int32 error_code = 2;
string error_message = 3;
}
Behaving like a normal JWT validation, this process parse, decode, and compare the token hash value to verify the token signature authenticity. The data inside the JWT payload is then stored in local variables for further validations.
Every user has a list of allowed IP address stored in a field in the Firestore document. If the user has the same IP address as the one in the request message, the validation passes. When a user has an IP of 0.0.0.0/0 in the list, it always passes this validation. IP whitelist can be entirely disabled from the operator service.
JWT Token of a logged in user is stored in the database. When an authorization check is requested and the token value in the message is different with the one stored in the database, the validation fails. This is done to avoid valid token in multiple device or session. The token from the latest login is always be the valid one.
The last step of the validation is the privilege validation. Incoming validation access request comes with a privilege code of the endpoint. It is then compared to the list of privileges in the group where the user belongs to. When the group has the privilege code, the validation passes and this method will return a response with isAllowed set to true, which means the token is valid to access the endpoint.
Implementing authentication and authorization in a service requires a service to be a gRPC client to the User Service. the rpc method is then invoked in the HTTP auth middleware located in internal/business/web/v1/middleware/jwt.go.
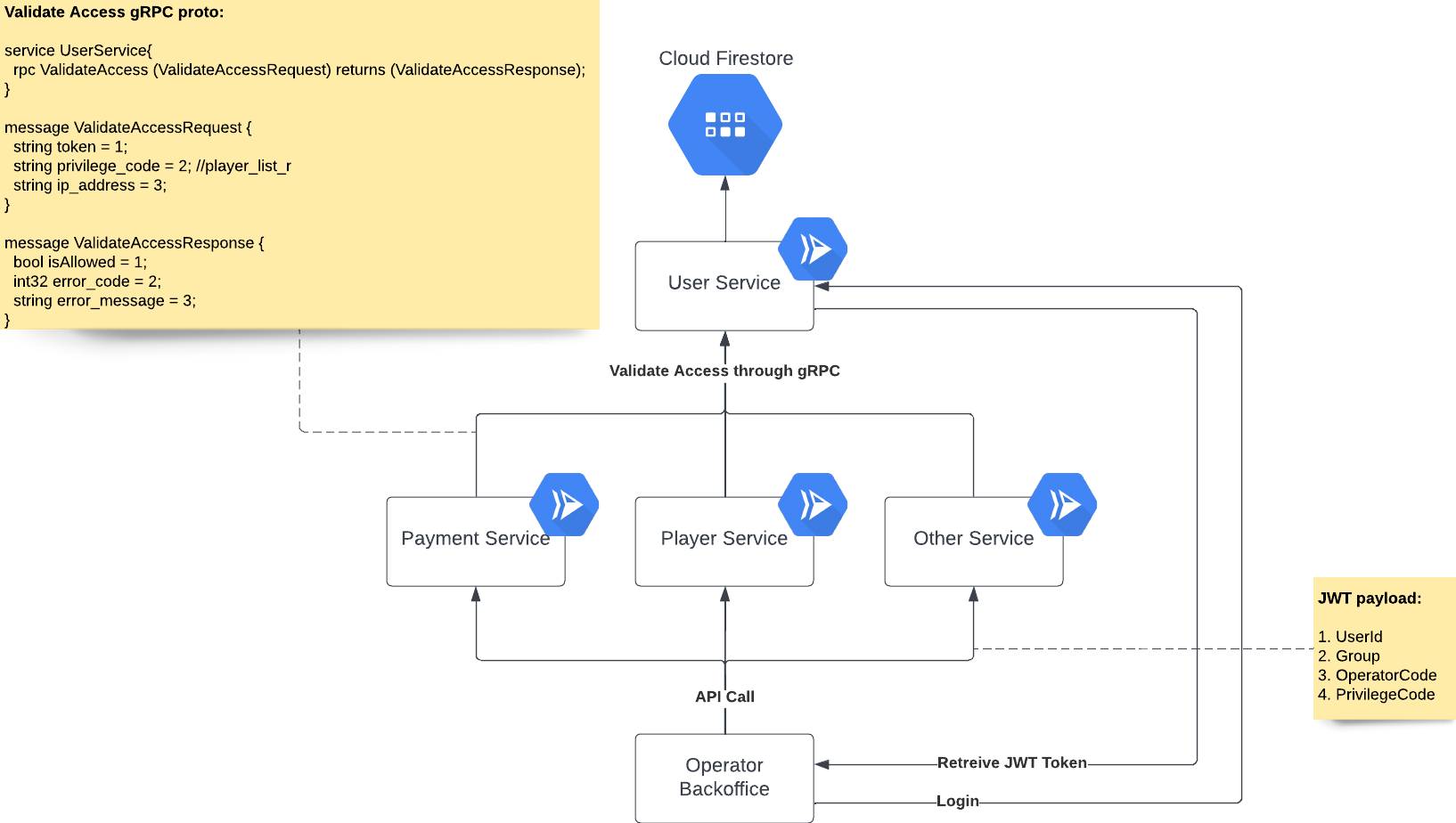
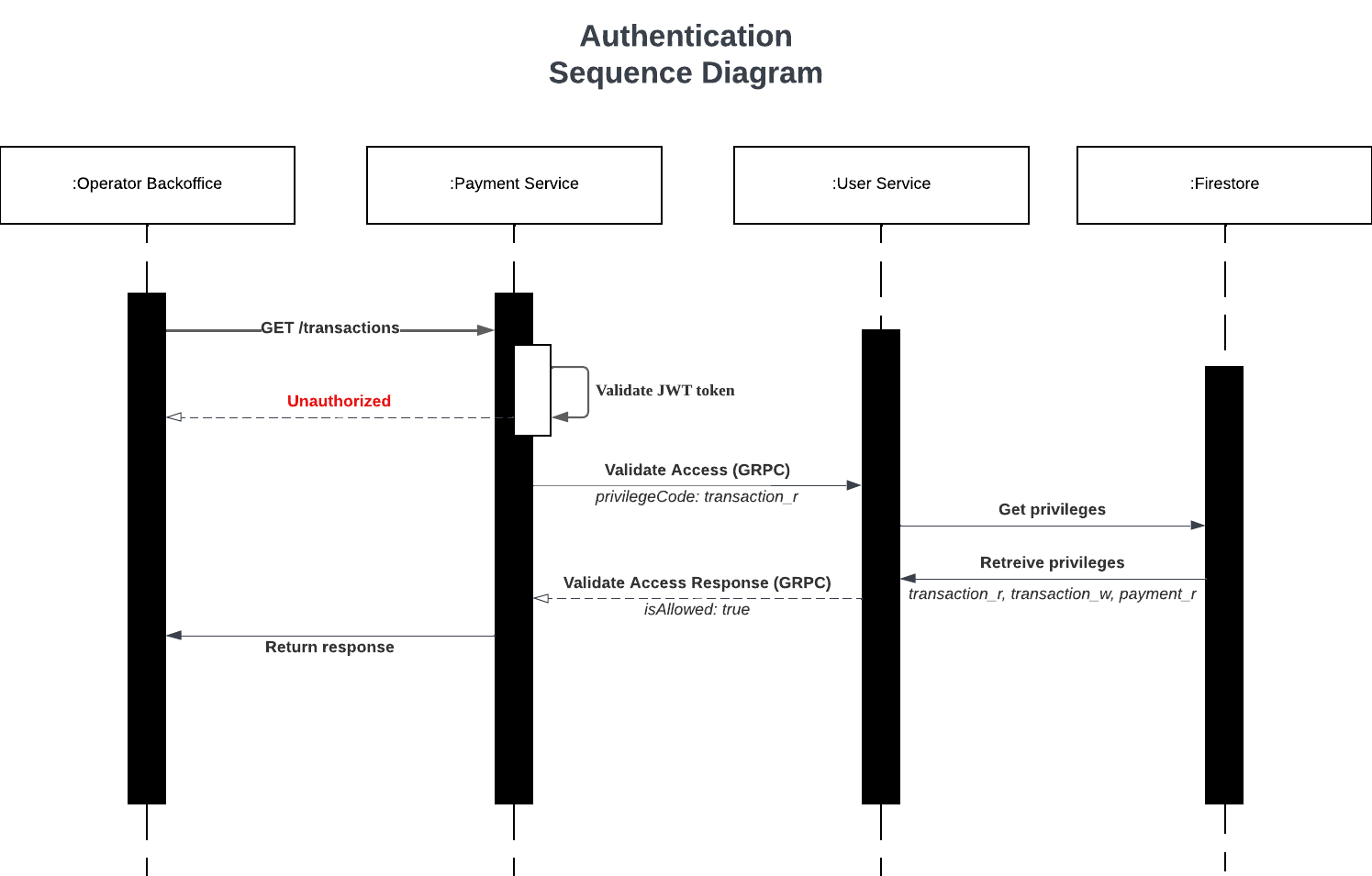
Every protected endpoint has a privilege code. For example, /transactions endpoint has a privilege code trx_r and accessing that endpoint require a Bearer Token from a user who belongs in a group that has the privilege for trx_r.
Privilege code consists of the model, context, or service and a letter representing the action -- c for create, r for read, and u for update. In the previous example, trx represents transactions data in the payment service and r represent the read access to the service.
The list of privileges for endpoints is described in internal/business/web/middleware/roles-guard.go on all services. Below is the example file in Report Service. The list is set to a variable RolesGuard with a type of nested maps map[string]map[string]string. The key in the first level of the map is the HTTP method, followed by the path, and then the privilege code.
package middleware
var RolesGuard map[string]map[string]string = map[string]map[string]string{
"POST": {
"/gameRound": "gmRound_c",
},
"GET": {
"/gameRound": "gmRound_r",
"/player-winlose": "plyrWinLoss_r",
"/provider-winlose": "provWinLoss_r",
"/player-round-details": "plyrTo_r",
"/outstanding/:playerKey": "plyrTo_r",
"/operator-summary": "sum_r",
"/player-summary": "sum_r",
"/transactions/:playerKey": "sum_r",
"/transaction/:playerKey": "sum_r",
},
}